Precious Metal Recovery (PMR)
Overview
We employ cutting-edge technologies at our facilities to meet customer demands for secure and transparent processing of an ever-increasing variety of electronic waste materials.
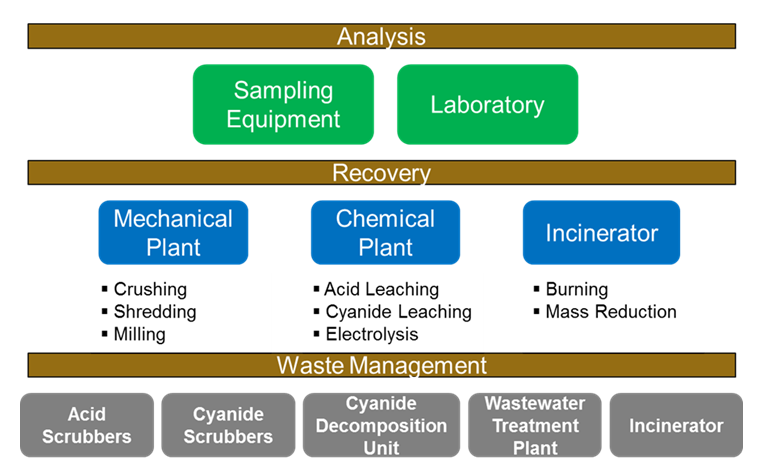
Our Processes & Facilities
Sampling Equipment
Sampling is fundamental to the precious metal recovery process because the assays determine the precious metal content of the customers’ materials and consequently the value of the precious metal content for financial settlement.
Laboratory
Besides its use in the assaying of customers’ materials, our in-house laboratory fundamentally ensures optimal performance of our recovery processes, thus maximising precious metal recovery. Customers’ materials are sent to our in-house laboratory for chemical analysis to determine their precious metal content. Our laboratory uses a combination of drying, crushing, milling, screening and dividing equipment to prepare representative samples for chemical leaching, followed by metal determination using Inductive Coupled Plasma (ICP-OES).
Our laboratory will carry out gravimetric testing on case-to-case basis for samples with high gold or platinum content.
Mechanical Plant
Some precious metals are imbedded within electronic components or printed circuit boards. Inaccessible from the surface, they need to be liberated before they can be recovered. This is done in our mechanical plant where crushing, shredding and milling machines are available to break down customers’ materials to size. Built-in dust collectors minimises the emission of dust into the environment.
Different crushers provide the flexibility of handling various loads, throughput and material types, giving us the capability of handling a wide range of common electronic scraps.
Chemical Plant
Some precious metals cannot be liberated from electronic materials by physical means. They require chemical processing. Our chemical plant consists primarily of acid leaching and electrolysis lines; and a secondary line for recovery, refining and melting of precious metals to produce ingots.
Acid leaching extracts precious metals that are embedded in solid electronic scraps. Materials are fed into this tank where they are dissolved. The precious metals present in the liquid are then extracted by selective precipitation.
Cyanide leaching removes gold from materials with surface or visible gold (eg. smart cards, BGA chips, connector pins, etc.). As this process involves cyanide, all relevant safety and security measures are strictly implemented and adhered to for maximum safety to operators and the environment. Materials are placed into titanium baskets and then submerged into a cyanide-based solution for selective removal of surface gold. The resulting gold-saturated solution is then sent for electrolysis for further gold recovery.
Electrolysis recovers gold from gold-saturated solutions. Gold present in the solution are plated onto the cathodes. The resulting gold flakes are then removed from the cathodes for further refining.
Incinerator
Some materials are light (eg. filters, rags and wipes, from plating operations) and cannot be mechanically crushed or chemically stripped. Our specially-designed incinerator is used for mass liberation of precious metals from such materials. Post-incineration residue is then transferred to the chemical process for further precious metal recovery.
Get Started Today
Contact us today for a free consultation.
